SOLAR ELECTRONICS
Solar Electronics
A solar power system has several key components, including solar panels, mounting structure, solar inverter, cables, connectors, and a solar battery if it is an off-grid module. While solar PV panels are often considered the most crucial element of solar energy solutions, even the inverter plays a vital role in solar power generation.
Solar inverters are electrical devices designed to convert Direct Current (DC) harnessed by the PV solar panels into Alternating Current (AC). Since both household and commercial appliances such as air conditioners, fans, geysers, washing machines, and refrigerators require Alternating Current (AC) to function and solar panels produce Direct Current (DC), solar inverters carry out the conversion process.
Although the primary purpose of solar inverters is to Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC), today, inverters come with other advanced capabilities such as utility controls and data monitoring, helping you keep tabs on your solar panel system.

The Various Types of Solar Inverters
While all solar inverters have the same function, you can choose a variation depending on which solar power system you install, plus your unique power requirements. Solar inverters can be categorized into the following 3 types:
- Grid-Tie Inverter/On-Grid Solar Inverter
- Off-Grid Solar Inverter
- Hybrid Solar Inverters
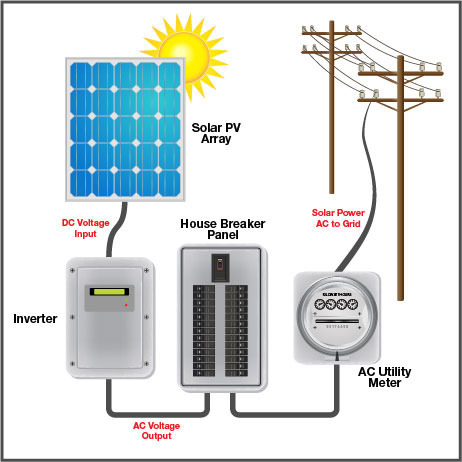
1. Solar On-Grid Inverter
As the name suggests, on-grid or grid-tie solar inverters remain connected to the local power grid, which is why these inverters only function when both grid and solar power is available. Additionally, any excess solar electricity is sent back to the grid, resulting in savings on utility bills. This cost-effectiveness makes on-grid solar systems, including on-grid inverters, more popular and economical.
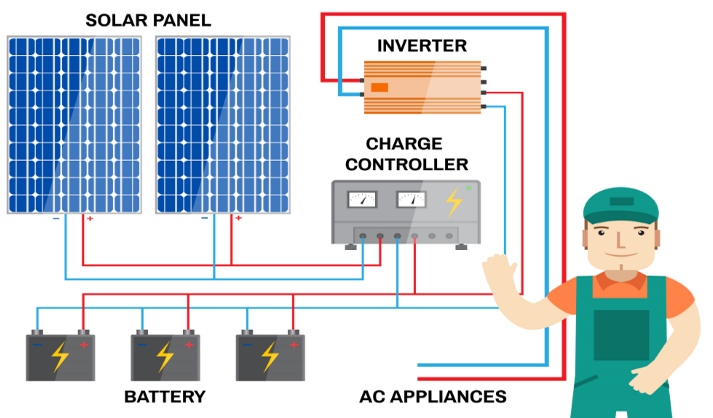
2. Off-Grid Solar Inverter
An off-grid solar inverter, also sometimes referred to as a stand-alone solar inverter, is independent of the local power grid, unlike grid-connected inverters. Traditionally used with off-grid solar power systems, this inverter solely functions on the solar energy produced by the photovoltaic panels. However, any excess electricity is sent to the solar battery instead of the grid, giving you sufficient power backup during outages.
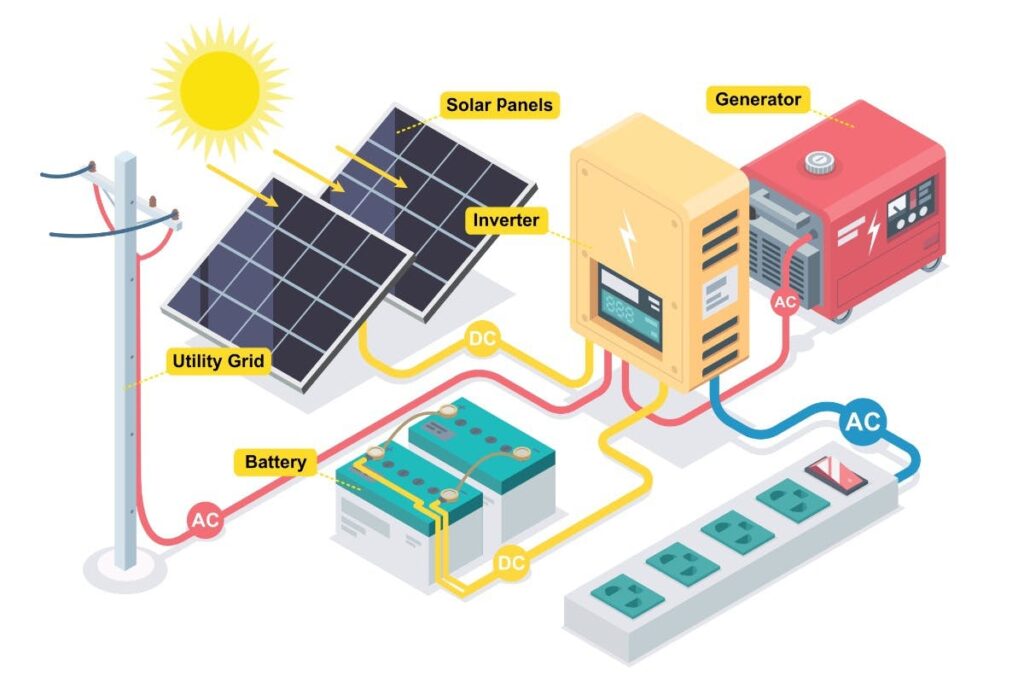
3. Hybrid Solar Inverter
Although quite similar to grid-tie PV inverters, hybrid solar inverters are somewhat complex. This is because the hybrid solar power system can simultaneously use multiple power sources like solar PV panels, local grids, and battery storage. However, these solar inverters primarily function on solar power but shift to the local grid when solar energy cannot be generated like during the night.
Solar Inverter Technologies
Once you’ve figured out which solar inverter will work best for you, the next step is to choose the inverter technology. Whether you’re buying an on-grid solar inverter or an off-grid inverter, there are two types of technologies available in the Indian market:
PWM Solar Inverters – The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) technology is best suited for off-grid solar inverters with a rating of less than 2KW. Typically used in remote and rural areas, off-grid inverters built with PWM technology are efficient yet economical.
MPPT Solar Inverters – The Maximum Power Point Tracker (MPPT) technology comes built-in with on-grid/grid-tie inverters. While MPPT-enabled solar inverters are highly efficient, they are also comparatively expensive than Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) technology.
